IN THIS ARTICLE
Light Component
The Light component simulates soft studio light with various types of punctual and area lights. The Light component supports the punctual lights Point (simple punctual) and Spot (simple punctual), which are infinitesimally small. These are slightly more performant than their area light counterparts, but they produce simpler light effects. The Light component also supports the area lights Point (sphere), Spot (disk), Capsule, Quad, and Polygon. These most accurately simulate real-world light sources.
Light types
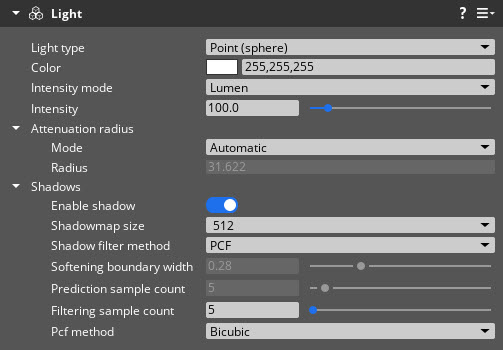
- Point (sphere)
- Emits light from the surface of a sphere in all directions, similar to a standard light bulb. The Point (sphere) light type supports shadow effects.
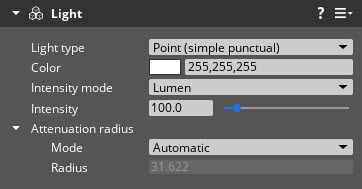
- Point (simple punctual)
- Emits light from a single point in space. The Point (simple punctual) light type is less photorealistic than the Point (sphere) light type, but Point (simple punctual) is more performant.
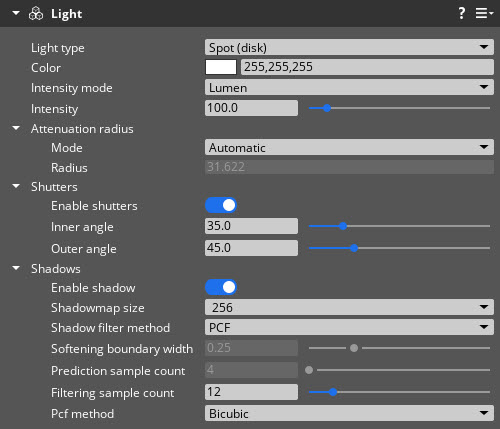
- Spot (disk)
- Emits light from a circle in 3D space, similar to a spotlight or recessed light. You can add shutters to constrain the light to a cone. The Spot (disk) light type supports shadow effects.
- Spot (simple punctual)
- Emits light from a single point in space constrained to a cone. The Spot (simple punctual) light type is less photorealistic than the Spot (disk) light type, but Spot (simple punctual) is more performant.
- Quad
- Emits light from the surface of a rectangle in 3D space. The Quad light type is most useful for illuminating a larger area with diffuse light. By default, the Quad light type uses linearly transformed cosines to calculate accurate lighting. It also supports a fast approximation calculation that’s more performant but produces lower-quality light. The Quad light type can emit light from one or both directions.
- Polygon
- Emits light from an arbitrarily shaped polygon in 3D space that are approximated by linearly transformed cosines. This polygon can have up to 64 points, but the Polygon light type becomes more expensive as the number of points in the polygon increases. The Polygon light type is the most expensive light type, but it produces very realistic area lighting. The Polygon light type can emit light from one or both directions.
Provider
Dependencies
Depending on the light type, the Light component has the following dependencies:
- Point (sphere): Sphere Shape
- Point (simple punctual): None
- Spot (disk): Disk Shape
- Spot (simple punctual): None
- Capsule: Capsule Shape
- Quad: Quad Shape
- Polygon: Polygon Prism Shape
Properties
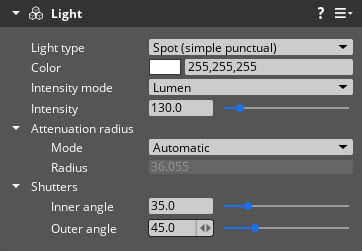
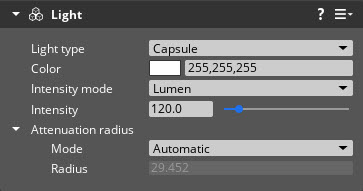
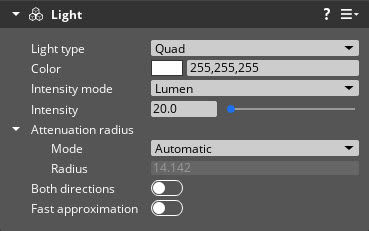
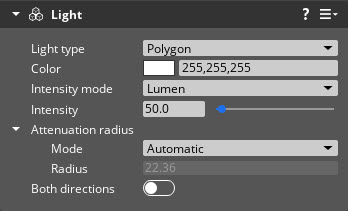
Base properties
| Property | Description | Values | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light type | The type of light. The properties vary for each light type. | Point (sphere), Point (simple punctual), Spot (disk), Spot (simple punctual), Capsule, Quad, Polygon | - |
| Color | The color of the light. Color acts as a gel on a pure white light and reduces the total energy output for light of any other color. For example, a 100 Lumen area light with a color setting of medium gray (18%) outputs only 18 lumens of light. | Eight bits per channel color: 0 to 255 | 255,255,255 |
| Intensity mode | The photometric unit of the light. Candela and Lumen specify the total amount of light energy that’s emitted from the entire surface area of the shape. If this mode is set as either Candela or Lumen, and Intensity is specified as 100.0, then the larger the provided shape component, the dimmer the light. This is because the total light energy is spread over a larger surface area. Nit represents light energy as candelas per square meter. Ev100 represents light energy as an exposure value over an area. Ev100 values are exponential, so a value of 5.0 Ev100 is twice as bright as a value of 4.0 Ev100. With Nit and Ev100, the larger the shape, the brighter the light. This is because the total light energy increases with the shape’s surface area. | Candela, Lumen, Nit, Ev100 | Lumen |
| Intensity | The light energy output or brightness in the photometric unit selected for Intensity mode. | Candela, Lumen, Nit: 0 to infinityEv100: -infinity to +infinity | 100 |
| Attenuation radius | Refer to Attenuation radius properties below. | Boolean | Disabled |
| Shadows | Refer to Shadows properties below. | Boolean | Disabled |
| Shutters | Refer to Shutters properties below. | Boolean | Disabled |
| Both directions | Enable this property to emit light from both sides of the shape. This field is available only for the Quad and Polygon light types. | Boolean | Disabled |
| Fast approximation | Enable this property to use a faster, lower-quality approximation for the lighting calculation, rather than the default high-quality linear transformed cosine technique. This field is available only for the Quad light type. | Boolean | Disabled |
Attenuation radius properties
| Property | Description | Values | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Specify whether attenuation is automatically calculated or explicitly set. Attenuation is the reduction of intensity of light energy as it travels, sometimes referred to as “falloff”. | Automatic, Explicit | Automatic |
| Radius | Define the attenuation distance for the light in meters. From a given point on the surface of an area light, the radius is the distance beyond which the light has no effect. If the Radius value is set too small for a bright light, it might result in non-photorealistic attenuation. This field is available only if Mode is set to Explicit. | 0 to infinity | 0.5 |
Shadows properties
Shadow properties are available only for the Spot (disk) and Point (sphere) light types.
| Property | Description | Values | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enable shadow | Enable shadow effects. | Boolean | Disabled |
| Shadowmap size | Set the width and height of the shadowmap. The shadowmap texture contains information about the light and objects in an area of the scene. It’s used for Shadow Mapping, a technique that renders shadows in the scene. A greater size results in a more detailed shadow effect. | 256, 512, 1024, 2048 | 256 |
| Shadow filter method | Set the shadow filtering method to reduce aliasing in the shadowmap. The supported methods are percentage-closer filtering (PCF) or exponential shadow maps (ESM). ESM+PCF uses ESM, but falls back to PCF in areas where ESM might fail. | None, PCF, ESM, ESM+PCF | None |
| Softening boundary width | To adjust the softness of the shadow edges, set the width in meters for the boundary between the shadowed and the lit area. If the width is 0, the soft edge is disabled. This field is available only if Pcf method is set to BoundarySearch. | 0 to 1 meter | 0.25 |
| Prediction sample count | The sample count used to predict whether the pixel is on the boundary. This field is available only if Pcf method is set to BoundarySearch. | 0 to 16 | 4 |
| Filtering sample count | The sample count used to filter the shadow boundary. This field is available only if Shadow filter method is set to PCF or ESM+PCF. | 0 to 64 | 12 |
| Pcf method | The PCF method used for shadows. The boundary search method performs a variable number of taps. The first tap determines if you’re on a shadow boundary, and the remaining taps find the occlusion amount. The bicubic method uses a fixed-size PCF kernel with kernel weights that are set to approximate bicubic filtering. This field is available only if Shadow filter method is set to PCF or ESM+PCF. | BoundarySearch, Bicubic | Bicubic |
Tips
For shadow effects, the different properties and filter methods have varying impacts on performance and quality. Using PCF with the bicubic method provides the best compromise between performance and quality.
A Shadowmap size of
512produces a result that balances quality and performance. The256size produces lower-quality shadows. The1024and2048sizes produce excellent quality, but they’re more expensive.
Shutters properties
Shutter properties are available only for the Spot (disk) and Spot (simple punctual) light types.
| Property | Description | Values | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enable shutters | Enable shutters to constrain the light to a cone shape. This field is available only for the Spot (simple punctual) light type. | Boolean | Disabled |
| Inner angle | Set the inner cone angles in degrees. | 0.5 to 90.0 degrees | 35.0 |
| Outer angle | Set the outer cone angles in degrees. | 0.5 to 90.0 degrees | 45.0 |
Notes
- When editing Light components, to see the shape and direction of the light, enable Debug Helpers in the Viewport.
