IN THIS ARTICLE
Grippers
Overview
Grippers are one of the most widely used effectors in robotic manipulation. The simulated robotic grippers are controlled by ROS 2 action servers that allow the user to track the current status of the gripping operation. The API to control the gripper through an action server is available in control_msgs .
Note:The grippers are available in theROS2ControllersGem.
Supported features
Two grippers are available:
- Vacuum gripper
- Finger gripper
Vacuum gripper
The vacuum gripper simulation is simplified and amounts to adding a fixed joint to the manipulated object, which needs to have a “Grippable” tag. Real vacuum grippers have limited range of effectiveness, because the seal that is essential to create a vacuum needs to be created through precise positioning. To simulate such behavior, Vacuum Gripper component has the following parameters:
- Effector Trigger Collider
- Effector Articulation Link
The effector trigger collider is an entity with a PhysX collider component.
The PhysX collider component has to be set to be a trigger. To learn more about triggers, please refer to
PhysX Collider component documentation.
The PhysX collider component needs to be adjusted to the expected range of the simulated gripper.
The sample configuration of the trigger collider is shown below:
The effector articulation link is an entity with PhysX Articulation Link.
This entity will be a parent forming a joint with the manipulated object.
You need to add a “Grippable” tag in
Tag Component to an entity for it to be gripped in the simulation. This prevents the gripper from attaching to the ground and other unintended objects: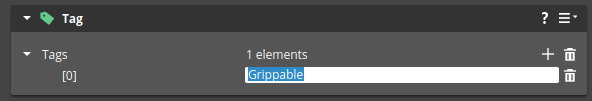
To summarize, here is a sample configuration of the vacuum gripper used in ROS2 Manipulation Template: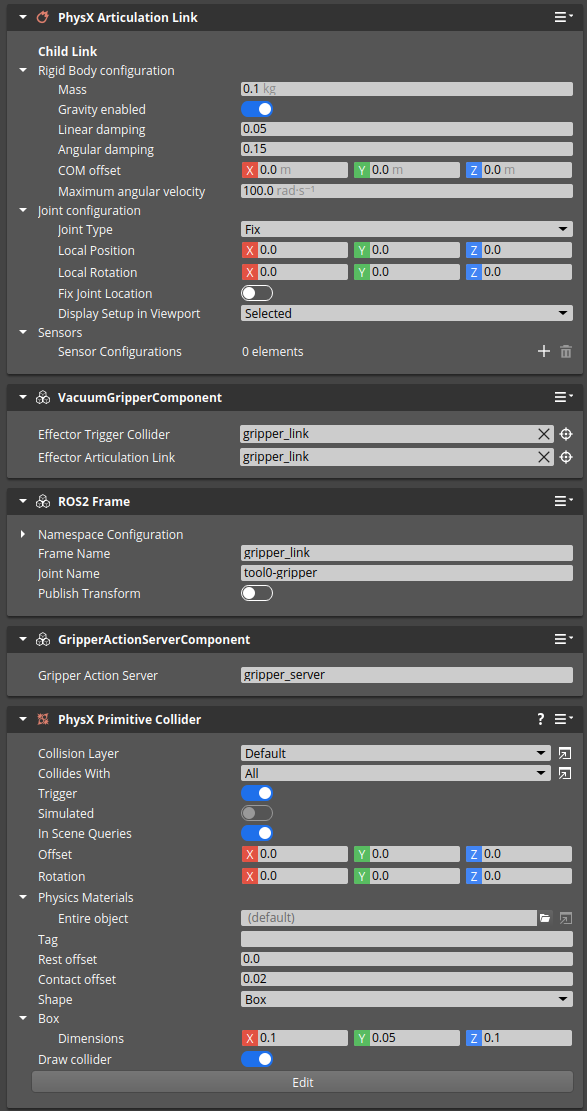
Finger gripper
Finger grippers are widely used in robotics and consist of at least two digits which can be brought closer to each other to capture an object. Finger gripper in ROS 2 Gem is simulated through collision and contact. It is a component that controls the motor at the top of the PhysX Articulation Link that is attached to the same entity tree.
The Finger Gripper component has the following parameters, which are necessary to fine-tune the behavior of the gripper:
- Velocity epsilon, which determines maximum velocity the gripper can have to still be considered stationary.
- Goal tolerance, which is the maximum distance the gripper can be from its goal position that still counts as reaching the goal.
- Stall time, a parameter used to determine if the gripper’s fingers are moving or not. This is the time that needs to pass to consider the gripper is stationary. In other words, short stall time can lead to reporting success prematurely.
Gripper action server
The Gripper Action Server component communicates with the Vacuum gripper or the Finger gripper and exposes their APIs as an action server to ROS. It allows you to configure the action server name.
Limitations
- Currently, both grippers work only with PhysX articulations.
- They can interact with rigid bodies and articulations but can be attached only to articulation links.
- Vacuum gripper is simple and can grip only objects with a “Grippable” tag.
Running with MoveIt2
You can configure the MoveIt2 framework to have a move group that can plan the movement of the gripper. Such a move group is implemented in ROS 2 launch file provided with Ros2RoboticManipulationTemplate . In provided example, change the “Planning Group” in “MotionPlanning” plugin for Rviz2 to “hand”. You can now move joints of the gripper using the “Joints” tag.
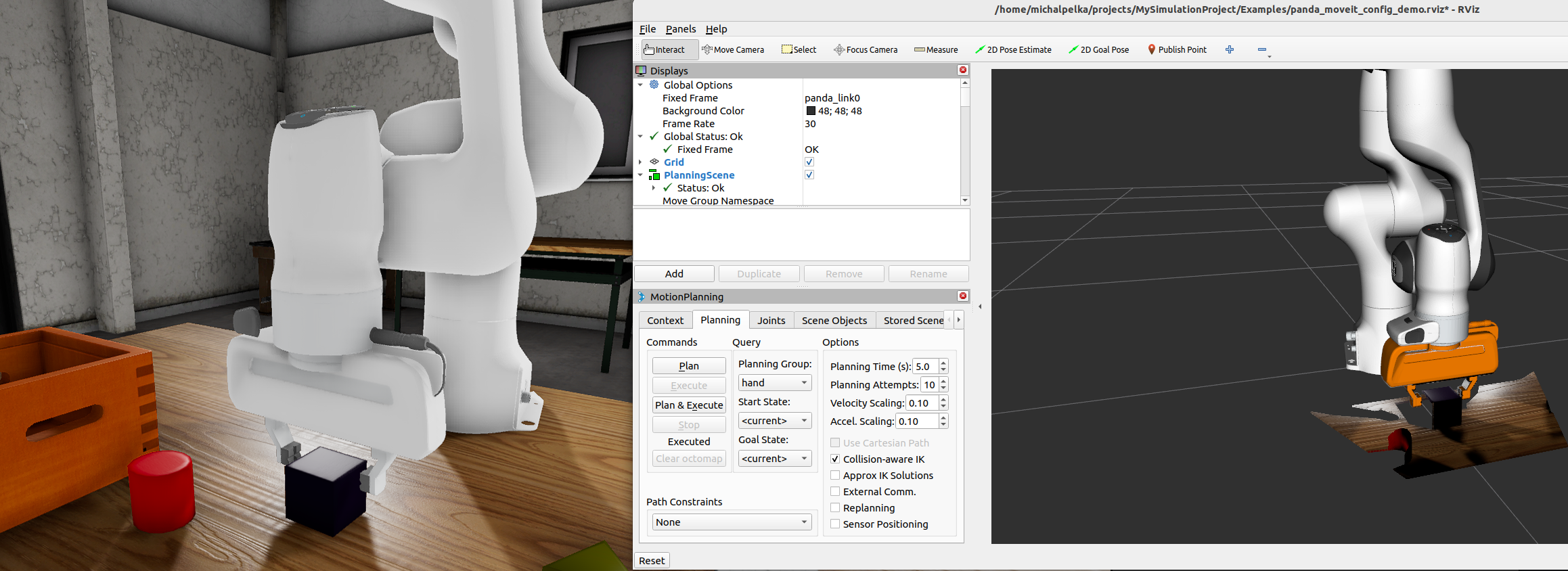
See Joints Manipulation to learn more about integration and control with MoveIt2.

