IN THIS ARTICLE
Script Canvas Execution Classes
Script Canvas offers a suite of classes to execute compiled graphs, with the goal of introducing as little execution overhead as possible to the execution of the graphs. The execution characteristics of graphs are determined at compile time, and can vary widely from graph to graph. The variations on managing their executions are encapsulated in a few classes to make it simple for the embedded programmer to execute and manage the lifetime of graphs in such a way to reduce or eliminate heap allocations and other possible performance costs.
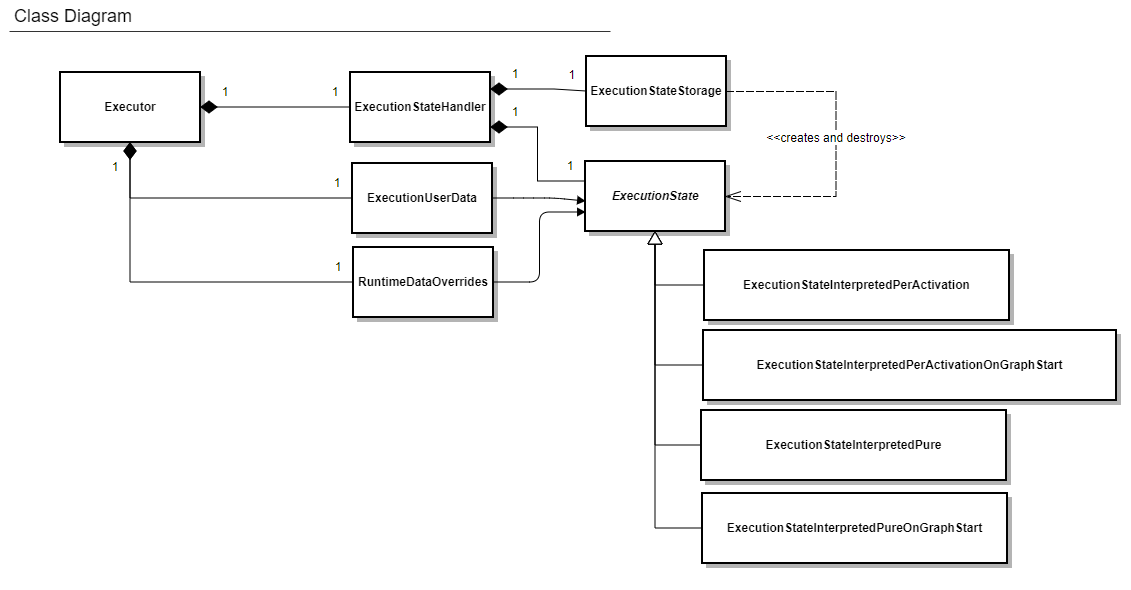
ExecutionState
ExecutionState is the abstract class which provides an interface for the actual runtime execution of compiled Script Canvas graphs. A compiled graph asset will store the traits which detemine which child class of ExecutionState will be required to execute it. Whether or not the graph defines pure functionality (it only defines methods that operate solely on their inputs), or defines state that will last beyond the execution of the initial function is read by ExecutionStateStorage and the appropriate child class of ExecutionState is created.
To execute a compiled graph, an ExecutionState object must be created with valid RuntimeData, RuntimeDataOverrides, and optional ExecutionUserData. Once constructed, the user must call Initialize() before calling Execute(). Finally, if required, the user can call StopExecution() before destroying the ExecutionState to stop execution of the required graph immediately. Not all of these methods will have any effect on all graphs. For example, if a graph is a simple “Print” Node after an “On Graph Start” Node, Initialize() and StopExecution() will be no-ops.
Since ExecutionState expects to run on a good runtime data provided to it with no overhead, it performs no safety checks against bad data. As an abstract class bordering on a pure interface, the ExecutionState object refers to, but owns as little as possible, any input it requires from the user to begin and maintain execution.
Developers who wish to embed Script Canvas runtime functionality somewhere in the engine where it currently does not exist only need to to use a properly configured ExecutionState object to do so. They can accomplish this however they wish, but O3DE provides some convienence classes (with performance in mind) to make the job easier. All of these convenience classes are used by the Script Canvas RuntimeComponent and the Script Canvas Interpreter. The RuntimeComponent is an example of the execution running after very strict safey checks for proper runtime data being provided. The Interpreter is an example of active, real-time, safety checking for valid runtime data, which might be under rapid iteration by a Script Canvas author.
What follows are descriptions of the convenience classes for embedding an ExecutionState.
ExecutionStateStorage
ExecutionStateStorage provides enough static storage space to allow the construction of any child class of ExecutionState without additional heap allocation. It is designed to be used with ExecutionStateHandler.
ExecutionStateHandler
ExecutionStateHandler provides RAII semantics for the ExecutionStateStorage and the ExecutionState owned by that storage. It also provides a measure of error reporting for the violation of safety checks if the developer embeds it in O3DE in such a way that it attempts to execute ScriptCanvas runtime data that is not valid. In non-release builds, this is enabled with the preprocessor macro, SC_RUNTIME_CHECKS_ENABLED. This macro turns on basic, minimal error checking and early returns, while minimizing branching at runtime. If the macro is disabled, the errors are written as asserts (if asserts are enabled in the build) with zero branching.
Executor
The Executor class hosts storage for all of the data required to run an ExecutionState object. It also provides the basic means of a safety check on execution, by allowing a developer to check if the ExecutionState that it owns is executable before trying to execute it. This is the class used by the RuntimeComponent and the Interpreter to run Script Canvas graphs.
